Project: Wood Studio House
Architect: Pablo Serrano Elorduy – Dom Arquitectura
Interior designer: Blanca Elorduy
Collaborators: Sebastia (Fustes)
Location: Sant Cugat del Vallès, Spain
Area: 76 m2
Photo Credits: Jordi Anguera
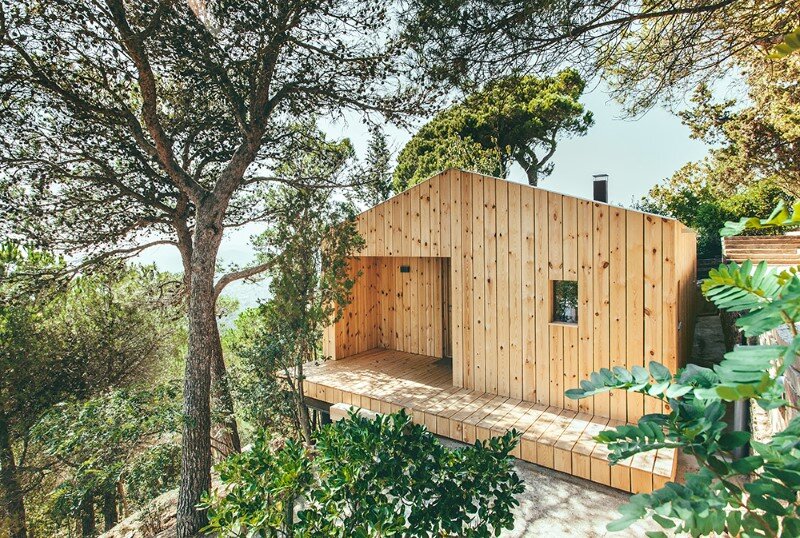
Wood Studio House is designed by Dom Arquitectura to accomplish four objectives: efficient, prefab, sustainable and passive. The house has 76 square meters and is located in Sant Cugat del Vallès, Spain.
Sustainable concepts:
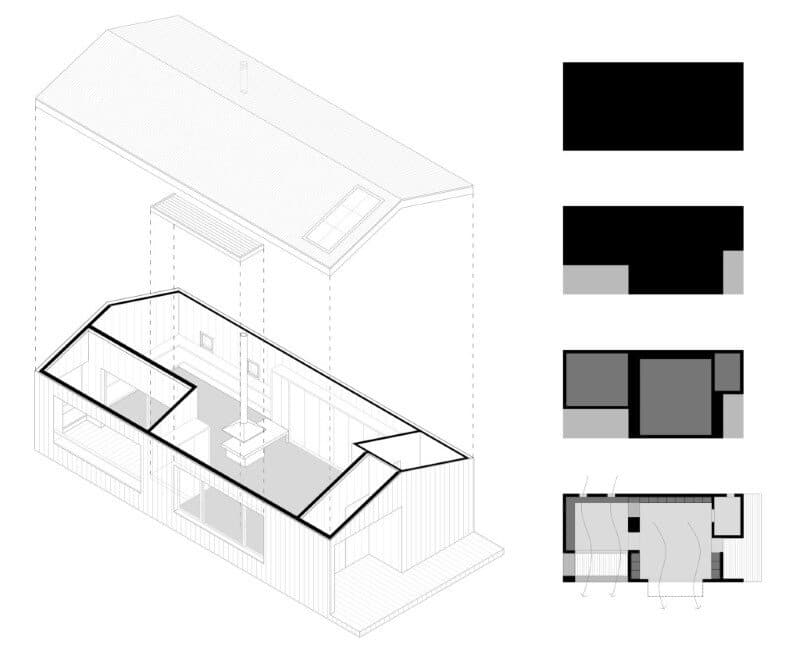
1. Orientation and compactness
The orientation and position of the house/studio have been studied in order to take the greatest advantage of the site’s available resources and climatic conditions, reducing its environmental impact, energetic consumption and improving its interior comfort.
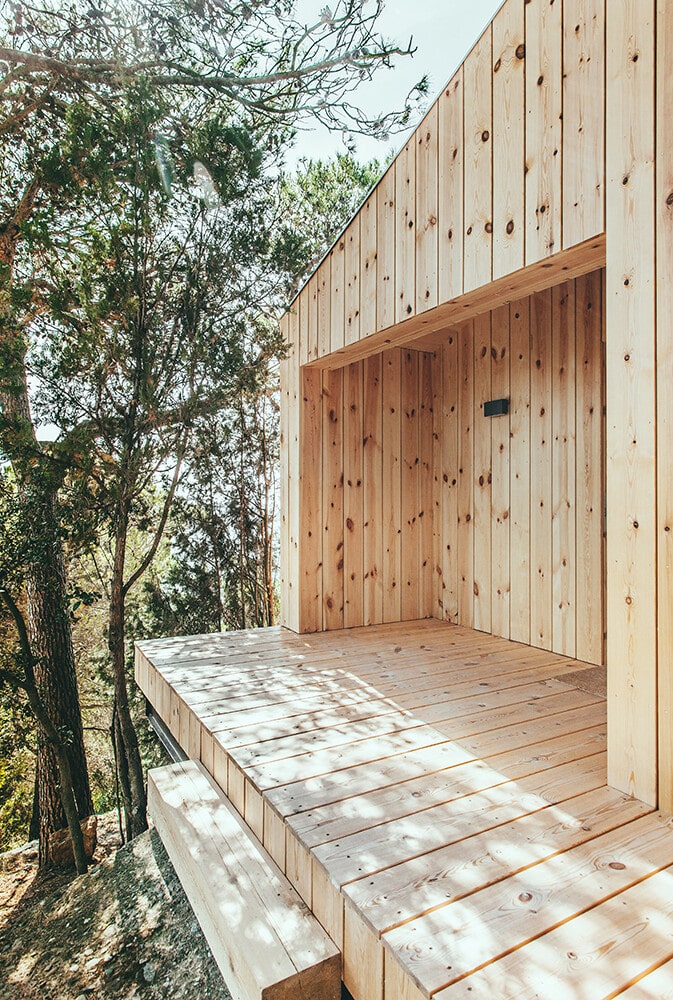
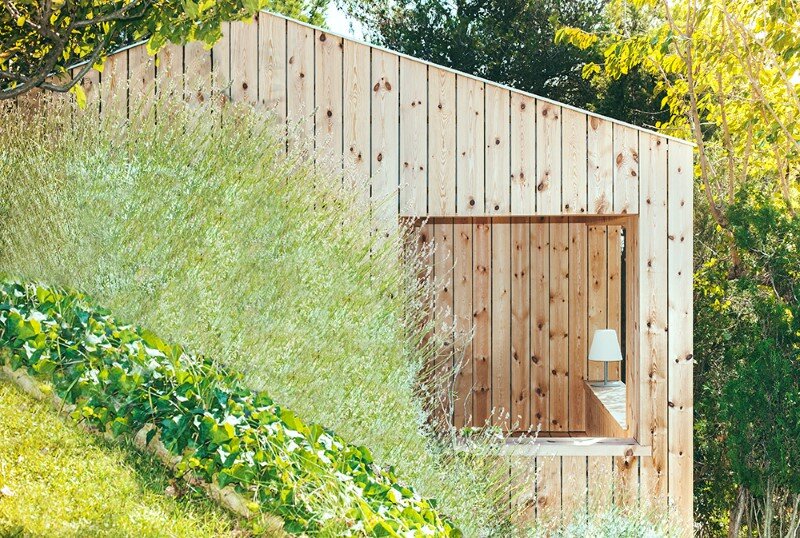
The Wood Studio House has a rectangular plan. Its longer side is oriented south, and has the biggest openings to capture radiation during winter months while protected from the sun during summer. The other 3 elevations are rather opaque, with few openings on the northern façade, which will create natural cross ventilation during summer.
The compact rectangular volume is only perforated at the terrace and porch, which allow for those two spaces to be covered and protected by the roof overhang. The compactness contributes to the energy reduction demands.
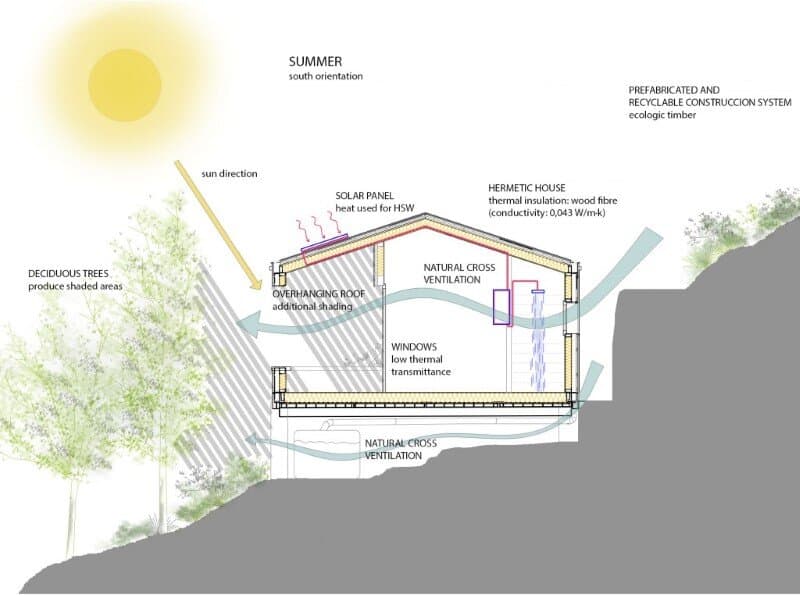
2. Sun protection and natural cross ventilation
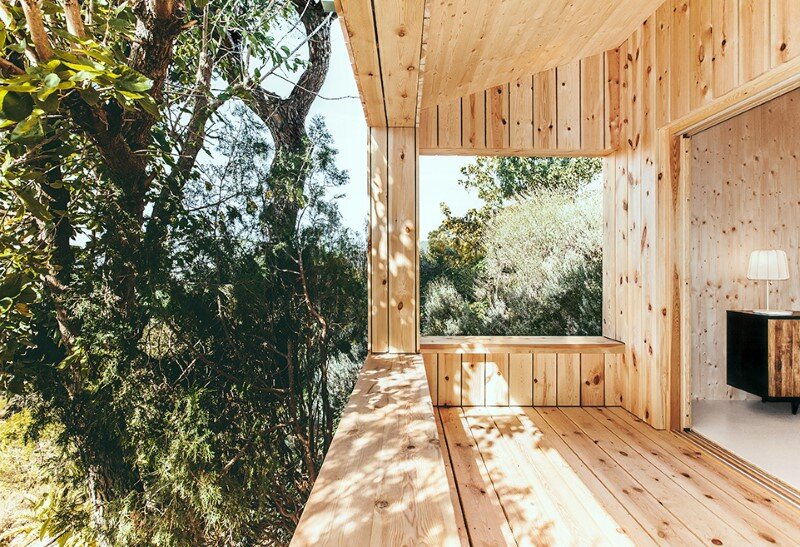
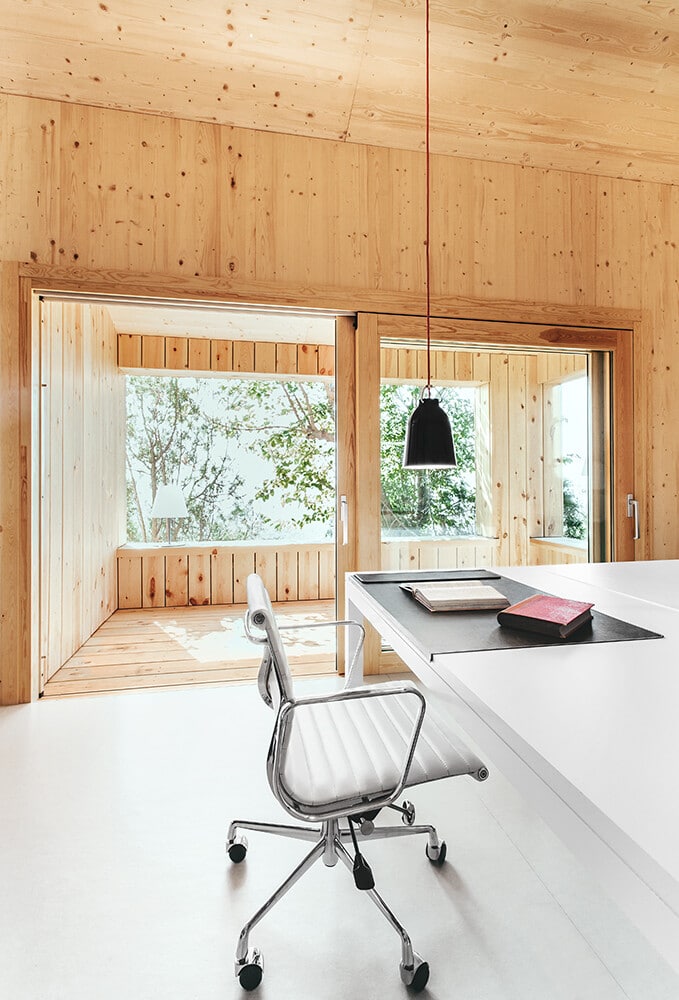
The south elevation possesses the biggest and best-protected openings against summer sunrays. The studio opening is protected by 2mts of roof overhang that prevent direct radiation during the hottest season. The big opening at the living room is designed in line with the outer wall; therefore, a 1mt deep sunshade overhang designed in wood is placed above it, to protect it from direct sunlight during summer.
The overhangs’ design and placement, allow the winter sunrays to enter the interior spaces helping the heating of the same. The temperature and pressure differences between south and north facades, produce a gentle cross ventilation through the openings at both these elevations. The openings, bigger at the southern façade, favour the thermal control of the interior spaces. Especially during the summer months, the natural cross ventilation will benefit the cooling of the main spaces.
The building technology and architectural elements used, as well as the general orientation and natural cross ventilation, result in fresh, dim and breathable interiors during the summer months.
3. Lifted to reduce its print
The Wood Studio House is placed on a south oriented steep slope. Existing is an older structure of concrete pilotis and steel beams that will be used as building foundations. The construction will therefore be lifted above the natural terrain, minimizing its environmental impact.
The timber technology chosen, has allowed the precise design and measurement of each and every element. All materials are locally available and found within the nearby area, which has decreased transportation costs and will allow for an easier reuse in the future.
These design moves have optimized resources and reduced waste, CO2 emissions and the overall environmental impact. The type of materials used is of low carbon emission, with low grey energy production and greenhouse effect.
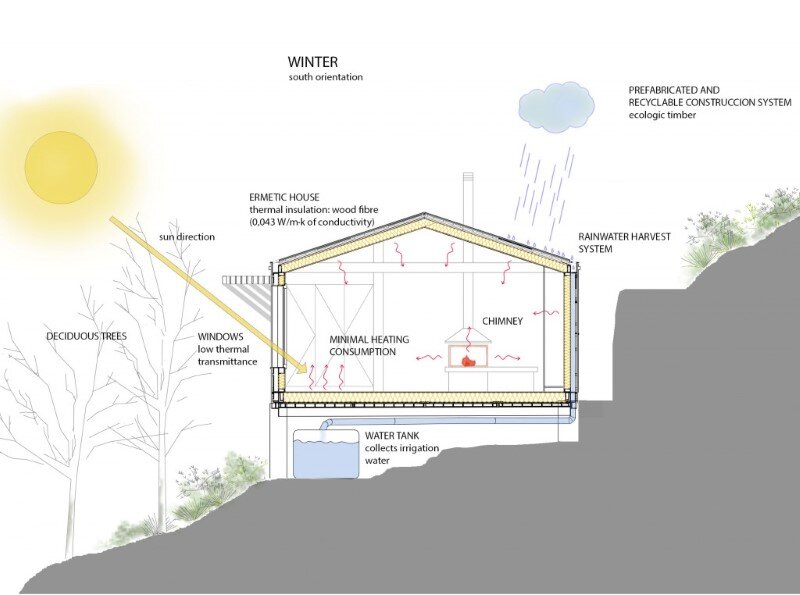
4. Rain water harvesting and irrigation tank
7 water tanks have been placed underneath the house. These can hold up to 10 cubic meters of water collected from roofs and exterior pavements. The water will later be used for irrigation of the lawns and the garden.
5. Ecologic kitchen garden
A kitchen garden has been designed to allow greater self-sufficiency of the house inhabitants. Taking advantage of the site and its natural environment, a garden has been planned in a flat extension attached to the house, where organic and healthy vegetables will be planted. Nearby, a small bees house has been built for the daily production of honey.
6. Seizing solar energy
Solar Panels have been placed on the roof to produce ACS for the bathroom, reducing energy consumption from the grid. Eventually the studio will be used as a house producing ACS on a daily basis.
Timber structure characteristics:
1. Prefabricated and reusable system
The construction process is based in prefabricated timber components. It is ecological and responsible with the environment. The timber used is recyclable, reusable, light and easy to mechanize. The system used for this project is a light structural framework in red pine wood. Due to the geographical location, and the site, all pieces have been assembled in situ while premade to measure in a workshop, facilitating its transport and join up.
All the timber comes from the Catalan Pyrenees, using local materials to reduce transport and consumption. All wooden pieces have been certified with the CE and CTB AWN TIMBER stamp and have the PEFC certification. These ensure a sustainable management of the forest resources. Wood is the only material that reduces CO2 emissions up to almost null once assembled and construction ended.
The walls’ thermal transmittance is of U=0.268 and the roofs’ is of U=0.207 reaching a A+ energetic qualification. The fire resistance of the structure is RF=30. The interior finishes are made in a three-layered plywood with pine finish, and the exterior finishes is in autoclaved treated fir wood.
2. Use of natural materials
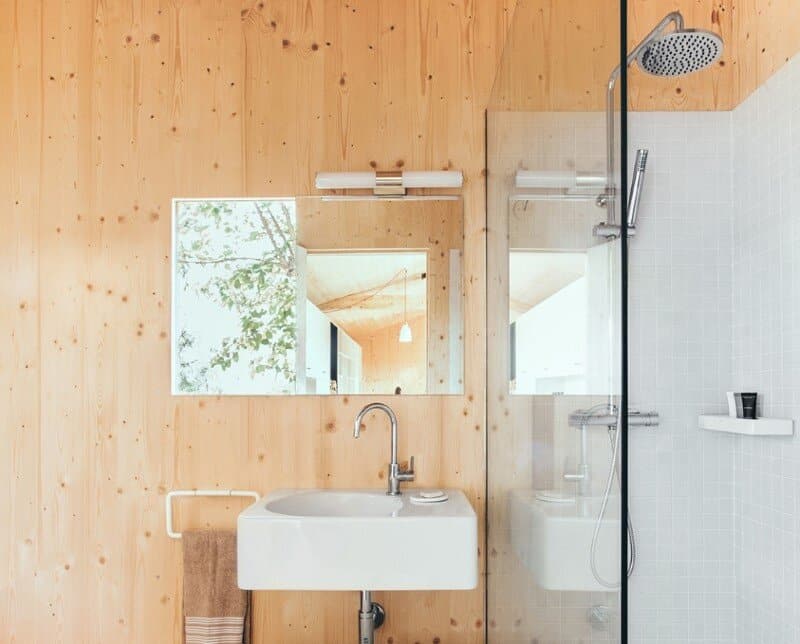
Timber is the main material used for structural purposes as well as for most of the interior and exterior finishes. Nevertheless the interior pavements are designed in linoleum, the only pavement lining offered in the market made mainly of renewable raw natural materials.
3. Thermal insulation
Thermal insulation prevents heat losses during winter and gains during summer due to a proper protection. The choice of timber as a main material plays a role in the general insulation of the construction. Timber has very low thermal conductivity, around 0.13. In addition, we have placed 16cm thick (instead of the regular 5cm used in the area) insulation in a natural and biodegradable material. The material chosen is wood fibre with a 0.043W/mK thermal conductivity and 50kg/m3 density. The insulation wraps around the whole construction with 12 cm in elevations and 12 in floors and ceilings.
4. Hermetic and watertight while breathable
The construction system used outfits the house with a highly insulating skin. These types of systems require a strong seal at every joint and opening creating in such a way a properly watertight and continuous layer. This will prevent any air escape or thermal bridge and will reduce energy waste. Around the whole house outer layer, a breathable layer is placed to allow the interior spaces to breathe allowing for steam to travel outside but not inside, preventing condensations and humilities.
5. Flexibility of uses
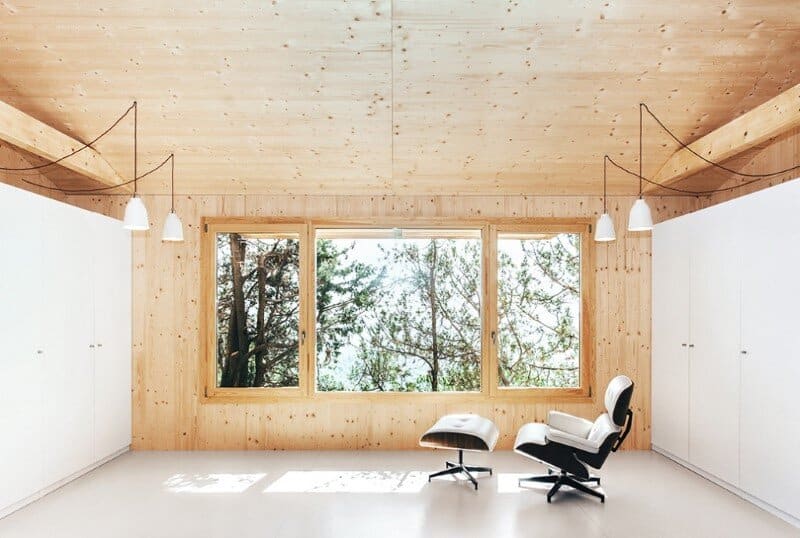
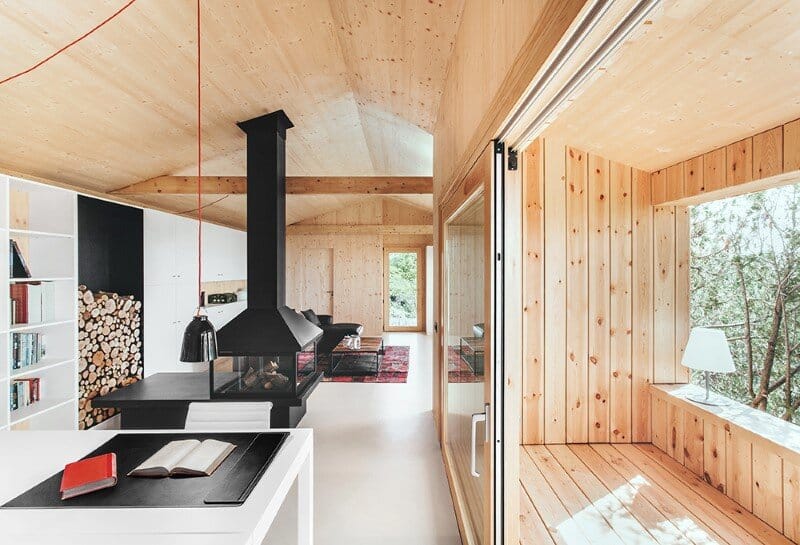
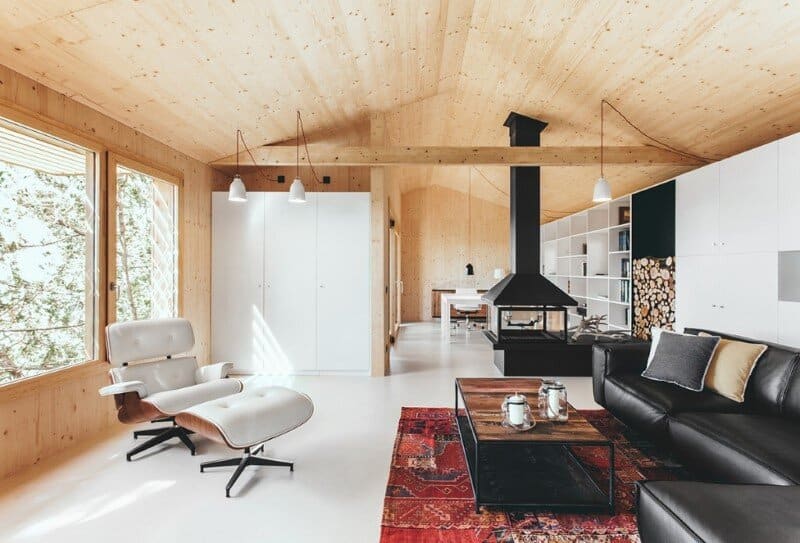
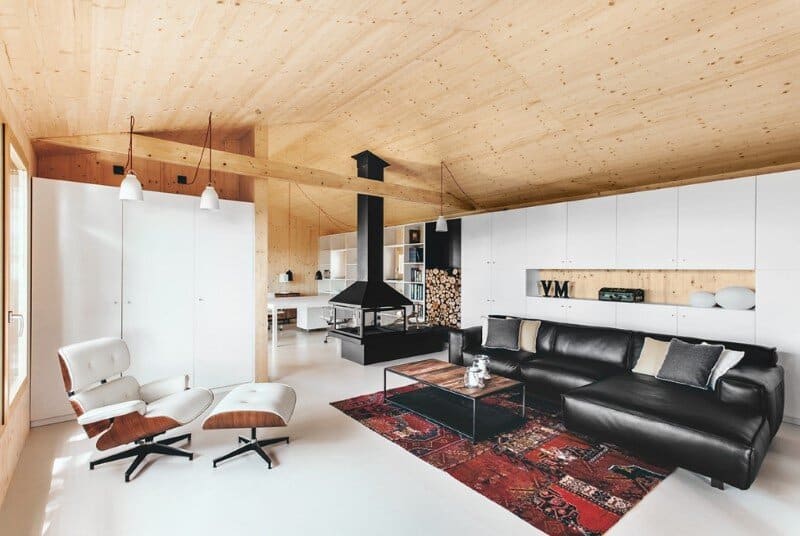
The house access is placed on its eastern side, where an entry platform is placed under a cover porch. The interior main space is a living room with access to a bathroom placed on the construction’s northwest corner. At the back we find the studio space, visually separated by a chimney whereas still open and connected.
The Wood Studio House has a covered terrace oriented south. The general distribution allows for changes overtime, eventually closing off the studio space and creating a separate room. The built in closets can potentially be transformed into a kitchenette, changing the use of the current studio into a little cottage.
6. Low thermal transmittance window frames
Tall exterior openings are executed with a high quality framing with thermal bridge breaking technology and double-glazing with low emission layers. The glazing used is of low thermal transmittance (U=1.5W/mk) greater protection than the CTE regulations. In addition they are placed on top of thermal insulation breaking any possible thermal bridge between exterior and interior.